The system’s RAM (Random Access Memory) prevents the PC from achieving its maximum capable performance. This occurs because the processor (CPU) is faster than the RAM, and usually it has to wait for the RAM to deliver data. During this wait time the CPU is idle, doing nothing (that’s not entirely true, but it fits our explanation). In a perfect computer, the RAM would be as fast as the CPU. Dual-, triple-, and quad-channel are techniques used to double, triple, or quadruple the communication speed between the memory controller and the RAM, thus increasing the system performance. In this tutorial, we will explain everything you need to know about these technologies: how they work, how to set them up, how to calculate transfer speeds, and more.
Before going further, let’s first explain how the RAM is traditionally connected to the system.
[amazon box=”B01NCE8T92,B079D3DBNM,B012M8LXQW” template=”table”]
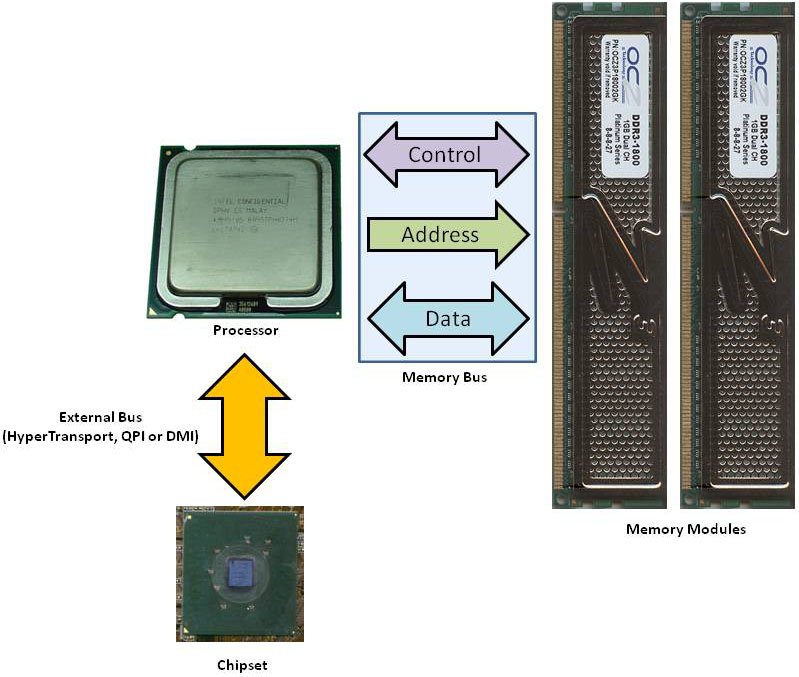
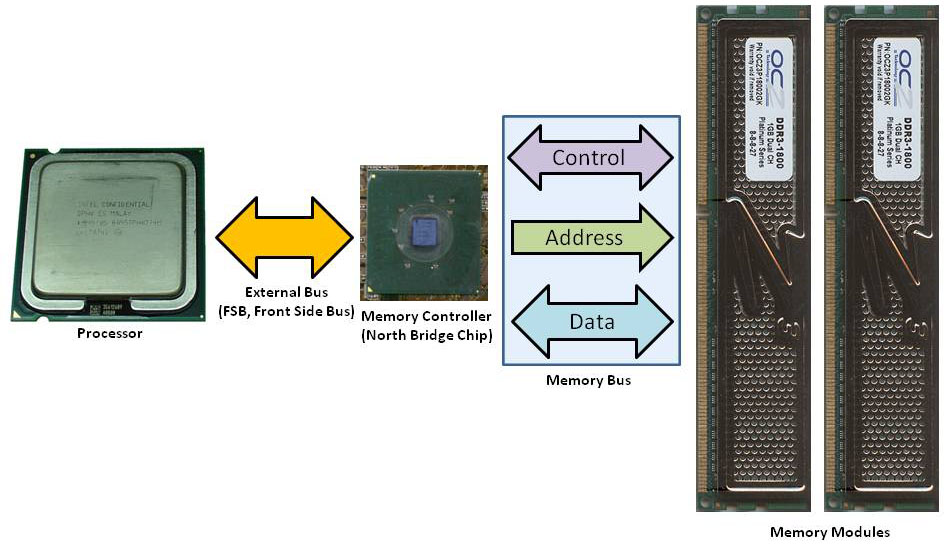
The RAM is controlled by a circuit called a memory controller. Currently, most processors have this component embedded, so the CPU has a dedicated memory bus connecting the processor to the RAM. On older CPUs, however, this circuit was located inside the motherboard chipset, in the north bridge chip. (This chip is also known as MCH or Memory Controller Hub.) In this case, the CPU doesn’t “talk” directly to the RAM; the CPU “talks” to the north bridge chip, and this chip “talks” to the memory. The first option provides better performance, since there is no “middleman” in the communications between the CPU and the memory. In Figures 1 and 2, we compare the two approaches.
The RAM is connected to the memory controller through a series of wires, collectively known as a “memory bus.” These wires are divided into three groups: data, address, and control. The wires from the data bus will carry data that is being read (transferred from the memory to the memory controller) or written (transferred from the memory controller to the memory, i.e., coming out of the CPU).
The wires from the address bus tell the memory modules exactly where (which address) that data must be retrieved or stored. The control wires send commands to the memory modules, telling them what kind of operation is being done – for example, if it is a write (store) or a read operation. Another important wire present on the control bus is the memory clock signal.
The memory speeds (clock rates), maximum capacity per memory module, total maximum capacity, and types (DDR, DDR2, DDR3, etc.) that a system can accept is defined by the memory controller. For example, if a given memory controller only supports DDR3 memories up to 1,333 MHz, you won’t be able to install DDR2 memories, and if you install DDR3 memories above 1,333 MHz (e.g., 1,866 MHz or 2,133 MHz modules), they will be accessed at 1,333 MHz.
(An exception to this rule is when the motherboard allows you to configure the RAM at a clock rate above the official maximum supported by the memory controller. For a real example, current Intel CPUs support memories up to 1,333 MHz, but several motherboards will allow you to configure clock rates up to 2,133 MHz.)
The discussion about clock rates is really important, because the clock rate defines the available bandwidth, which is our next subject.
[nextpage title=”Bandwidth”]
Bandwidth is the maximum theoretical transfer rate of a communications channel. In the case of memories, the bandwidth is measured in megabytes per second (MB/s) or gigabytes per second (GB/s), meaning how many millions or billions of bytes can be transferred per second, respectively. One byte is a group of eight binary digits or bits, i.e., a sequence of eight 0’s or 1’s. The memory bandwidth can be determined through the following formula:
bandwidth = real clock rate x data transferred per clock cycle x bits transferred per clock cycle / 8
Memories based on the DDR (Double Data Rate) technology, such as DDR-SDRAM, DDR2-SDRAM, and DDR3-SDRAM, transfer two data per clock cycle. As a result, they achieve double the transfer rate compared to traditional memory technologies (such as the original SDRAM) running at the same clock rate. Because of that, DDR-based memories are usually labeled with double their real clock rate. For example, DDR3-1333 memories actually work at 666.6 MHz transferring two data per clock cycle, and thus are labeled as being a “1,333 MHz” device, even though the clock signal doesn’t really work at 1,333 MHz.
You will need to use the real clock rate on the above formula, or you can simplify the formula as follows and use the DDR clock rate:
bandwidth = DDR clock rate x bits transferred per clock cycle / 8
Memory modules currently used are 64-bit devices. This means that 64 bits of data are transferred at each transfer cycle. Therefore, we will be using “64” as “bits transferred per clock cycle” in the above formula. Thus, we can simplify the bandwidth formula even further:
bandwidth = DDR clock rate x 8
That said, we can easily calculate the bandwidth of any memory. For example, DDR3-1333 memories have a bandwidth of 10,664 MB/s or 10.6 GB/s, and DDR3-1866 memories have a bandwidth of 14,928 MB/s or 14.9 GB/s.
It is very important to understand that these transfer rates are the available bandwidth, i.e., the maximum theoretical transfer rates. When we calculate them, we are assuming that a data transfer will occur at each clock cycle (i.e., on a DDR3-1333 memory, 1.3 billion transfers per second will occur), which in fact never happens, because the CPU isn’t transferring data 100% of the time. That is why when you measure the actual memory transfer from your system using a program such as Sandra, you always get a value lower than the maximum theoretical transfer rate.
The dual-, triple-, and quad-channel architectures work by increasing the number of data wires available in the memory bus, doubling, tripling or quadrupling the available bandwidth, respectively.
It is very important to notice that this performance increase is achieved only on the memory subsystem; doubling the theoretical memory performance does not translate into a computer that is twice as fast. Only a small percentage of this memory performance increase will be reflected on the overall system performance.
Let’s now examine exactly how each of those architectures work and how to enable them.
[nextpage title=”Dual-Channel Architecture”]
As we briefly discussed in the previous page, the dual-channel architecture expands the number of data wires available in the memory data bus from 64 to 128. This doubles the available bandwidth. For example, if you use DDR3-1333 memories, the maximum theoretical transfer rate is doubled from 10,664 MB/s (10.6 GB/s) to 21,328 MB/s (21.3 GB/s).
Each memory module, however, is a 64-bit device. Therefore, in order for the dual-channel architecture to work, you will need to install two memory modules in parallel, making 128 bits available.
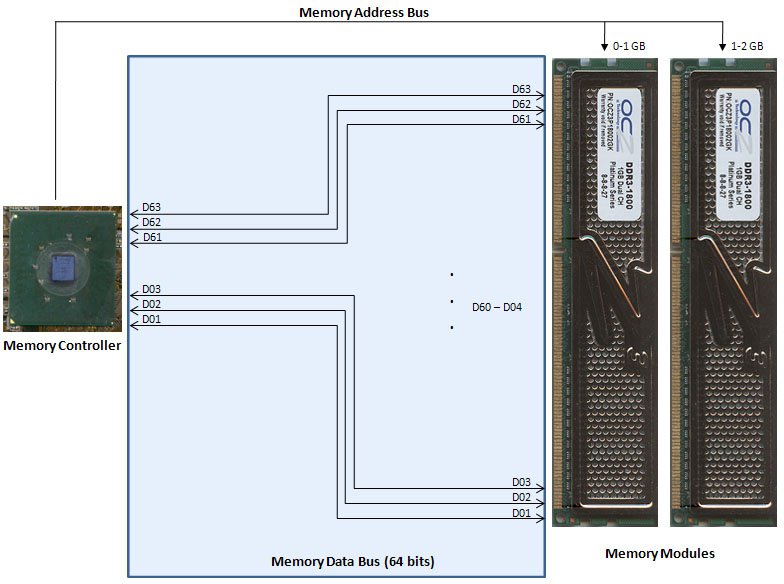
Many people have trouble visualizing this idea. Therefore, let’s draw some schematics. First, assume that we have a system that doesn’t support a dual channel feature (i.e., a single-channel system). In this case, the memory controller will transfer 64 bits at a time.
When we say that the memory data bus is 64 bits wide, this means that there are 64 wires (yes, physical wires on the motherboard) connecting the memory controller and the memory sockets. These wires are labeled D0 through D63. The memory data bus is shared amongst all the memory sockets. The address and control busses will activate the proper memory socket, depending on the address from where data must be stored or read. We illustrate this in Figure 3.
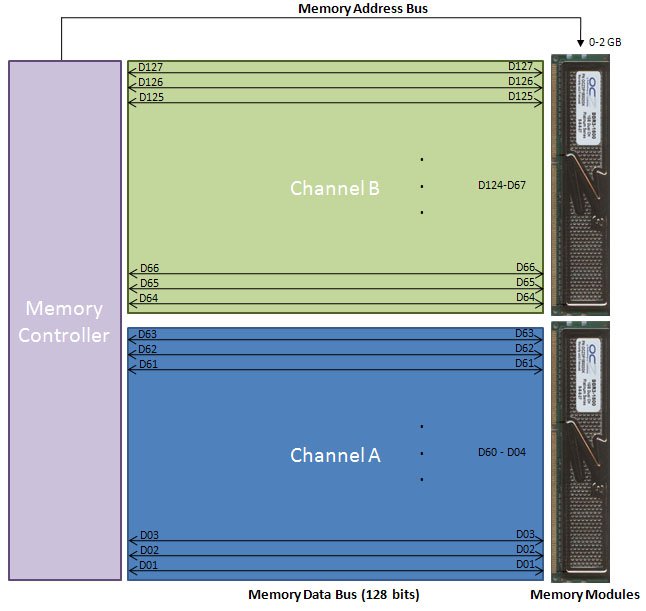
On systems supporting dual-channel technology, the memory data bus is expanded to 128 bits. This means that there are 128 wires connecting the memory controller to the memory sockets. These wires are labeled D0 through D127. Since each memory module can only accept 64 bits at once, two memory modules are used to fill the 128-bit data bus. See Figure 4. Because the two modules are accessed at the same time, they must be identical (same capacity, same timings, and same clock rate).
Now that you know what dual channel means, the most obvious question is: “How can I enable this architecture so I can increase my computer’s performance?” Let’s find out.
[nextpage title=”Enabling Dual Channel”]
In order to enable dual-channel architecture, you will need to have:
- Memory controller supporting dual-channel architecture (virtually all current CPUs support dual-channel architecture).
- Two or an even number of memory modules; each pair of modules must be identical.
- Install the memory modules in the correct memory sockets on the motherboard that will enable this architecture.
First, the memory controller must support the dual-channel architecture. As we discussed earlier, current CPUs have this component embedded, so almost all computers nowadays support this technology.
Second, you need to have an even number of memory modules on your system, as each pair of memory modules will be accessed as a single entity. Refer to Figure 4 in the previous page. If you install just one memory module, this technique won’t work because the memory will still be accessed at 64 bits per clock cycle. In other words, dual channel works by accessing two memory modules in parallel, i.e., at the same time. As each pair of memory modules is accessed as a single entity by the memory controller, the modules at each pair must be identical. Each pair, however, can have a different total capacity. For example, you can install two 2 GB modules and two 1 GB modules, for 6 GB total.
This is a very important point to keep in mind when selecting parts for building a PC. Let’s say you want to build a computer with 4 GB of RAM. In order to achieve the best performance, you must buy two 2 GB memory modules to enable dual-channel architecture. If you buy a single 4 GB module, you will have the same memory capacity; however, the memory will be accessed in single-channel mode, with half the bandwidth available.
The third point is to install the memory modules in the correct memory sockets on the motherboard. You have to be very careful; otherwise, you will buy two memory modules as recommended and end up having a system still accessing the memory under single-channel architecture.
In order to make our explanations easier to understand, let’s assume we have a motherboard with four memory sockets and the installation of two memory modules, which is the most common scenario. Number the motherboard memory sockets as one, two, three, and four.
The rules, however, depend on the kind of system you own. Intel, AMD socket AM3+, and a few AMD socket AM3 motherboards follow one rule, while all other AMD-based systems use a different rule. The following explains the differences between the two systems.
[nextpage title=”Enabling Dual Channel (Intel and AMD Socket AM3+)”]
Motherboards targeted to Intel CPUs and AMD socket AM3+ CPUs (and a few socket AM3 models) use sockets one and two as the first channel, and three and four as the second channel. In order to enable the dual-channel architecture, you have to install one module at the first channel and one module at the second channel. If they are installed in the same channel, you will have a single-channel architecture. Therefore, you must install the first memory module in socket one, and the second memory module in socket three, not in socket two. In other words, you have to skip one socket.
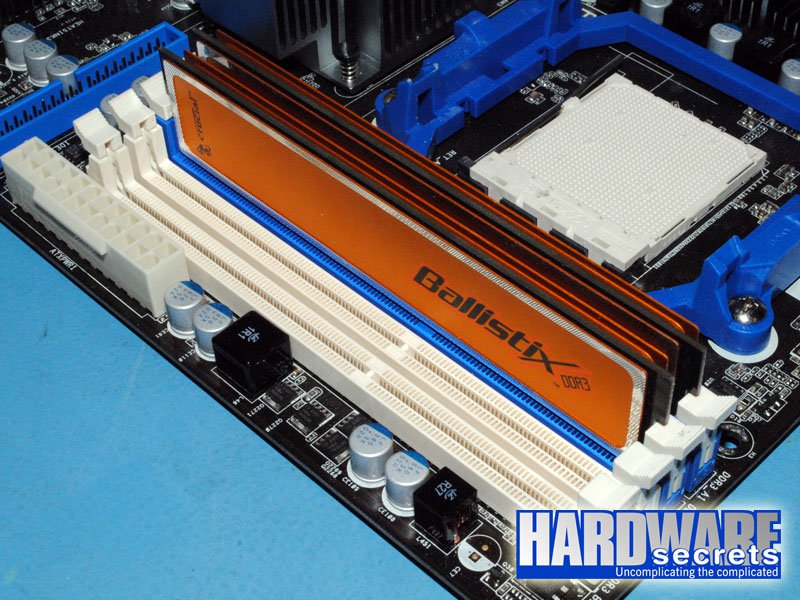
In order to make it easier for users, most motherboard manufacturers use different colors on the memory sockets, using one color for sockets one and three, and a different color for sockets two and four. This way, you need to install the memory modules in sockets with the same color. See Figure 5.
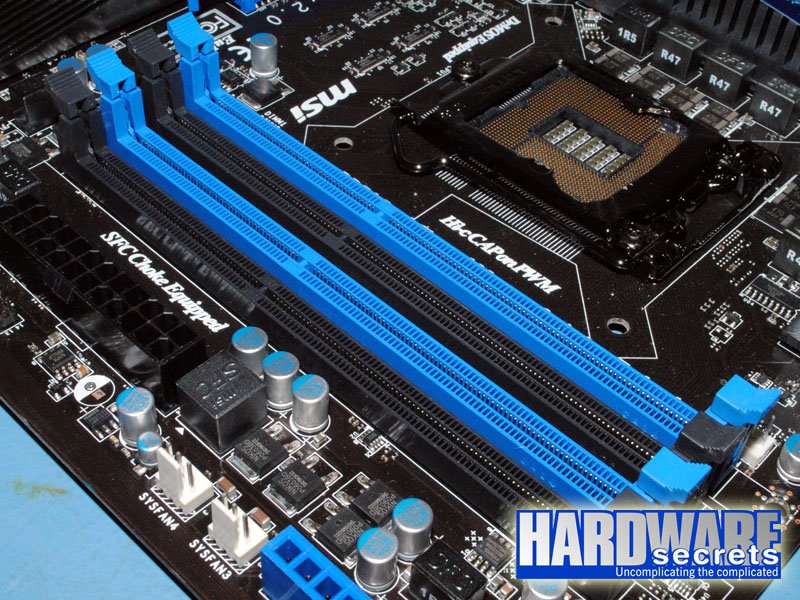
In Figure 6, you can see a motherboard for an Intel CPU with two memory modules correctly installed, enabling dual-channel architecture.
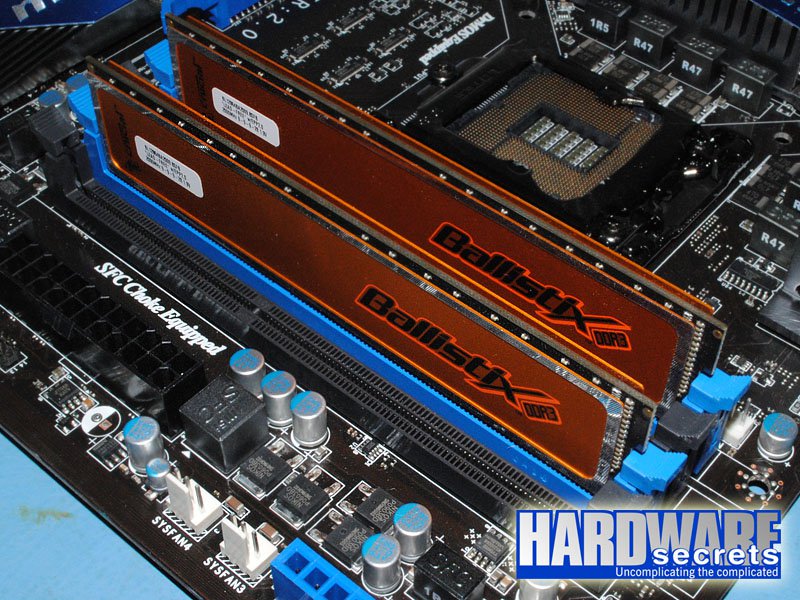
There is, however, one major exception. On some older motherboards from MSI targeted to Intel CPUs, sockets one and two use the same color while sockets three and four use another color. See Figure 7. If you install the two memory modules in sockets with the same color on a motherboard like this, they will work under single-channel mode, not dual-channel. So, if you find yourself in front of an older motherboard from this manufacturer, you should not follow the color scheme. You must install the memory modules in sockets one and three, and they will be using sockets with different colors.
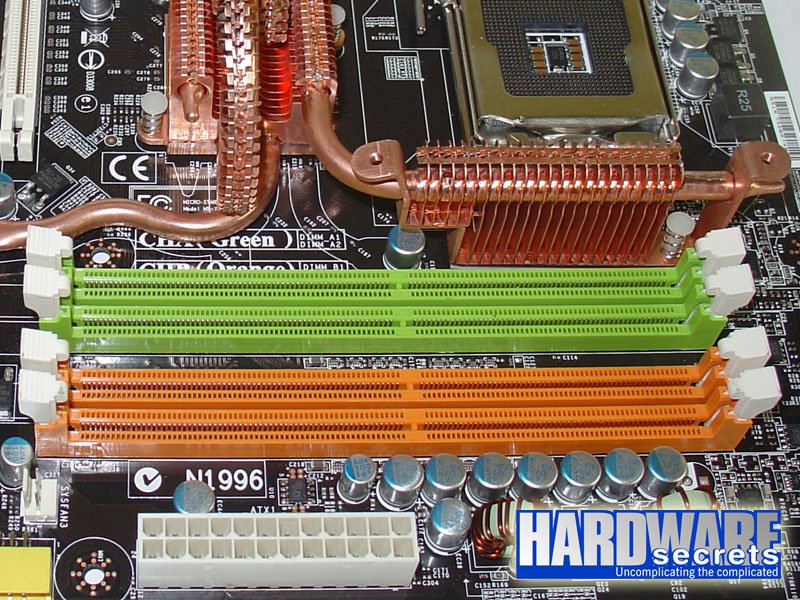
If you are installing four memory modules which are identical, there is no rule to follow. Simply install all four modules in the four sockets available.
However, if you are installing four modules and they have different capacities, you will have to pay attention. The first pair must be installed in sockets one and three, while the second pair must be installed in sockets two and four. By “pair” we mean two identical memory modules. In other words, install the first pair in sockets with the same color, and the second pair in the sockets using the other color.
[nextpage title=”Enabling Dual Channel (Other AMD Sockets)”]
Motherboards targeted to all other AMD CPUs use sockets one and three as the first channel, and two and four as the second channel. (A few socket AM3 motherboards follow the scheme presented in the previous page.) In order to enable the dual-channel architecture, you have to install one module at the first channel and one module at the second channel. If they are installed in the same channel, you will have a single-channel architecture. Therefore, you must install the first memory module in socket one and the second memory module in socket two. If you have four memory modules to install, simply install the second pair in sockets three and four.
The big difference is that, while on motherboards targeted to Intel and socket AM3+ CPUs you need to skip socket two when installing two memory modules, on motherboards targeted to all other AMD CPUs you need to install the memory modules sequentially.
In order to make it easier for users, most motherboard manufacturers use different colors on the memory sockets, using one color for sockets one and two, and a different color for sockets three and four. This way, you need to install the memory modules in sockets with the same color. See Figure 8.
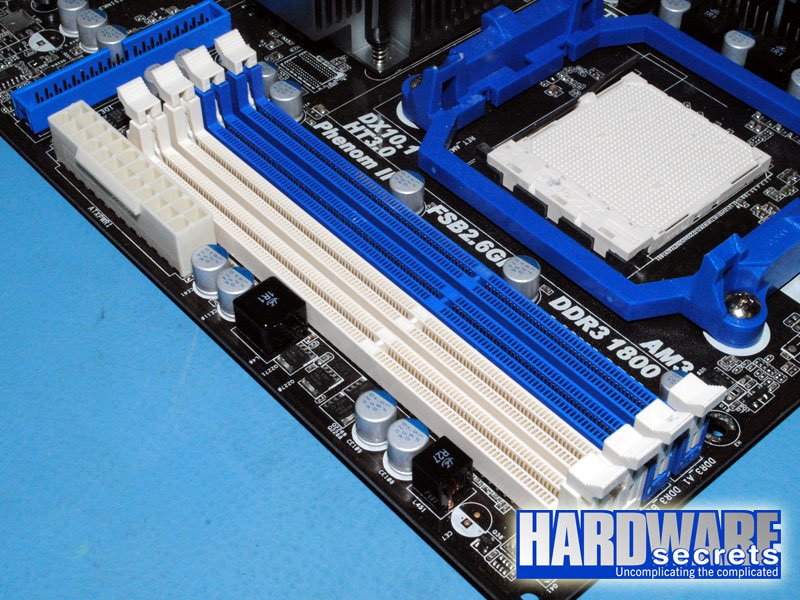
In Figure 9, you can see a motherboard for an AMD CPU with two memory modules correctly installed, enabling dual-channel architecture.
[nextpage title=”Triple-Channel Architecture”]
As you can assume by the name, the triple-channel architecture triples the available memory bandwidth. This is done by expanding the memory data bus to 192 bits, which is accomplished by accessing three memory modules at the same time.
Currently, this mode is available only on the Intel socket LGA1366 (LGA1366) platform. This means that you can only enable this mode on motherboards and Core i7 CPUs that use this socket. These processors support DDR3 memories up to 1,066 MHz.
You will need three identical memory modules. Six modules can be used on motherboards with six memory sockets, and each group of three modules can have different capacities, but the modules inside the same group must be identical. If you install two memory modules, they will be accessed in dual-channel mode. In this case, you won’t achieve the maximum performance of which your system is capable.
There are two kinds of socket LGA1366 motherboards available: those with four memory sockets and those with six or more memory sockets.
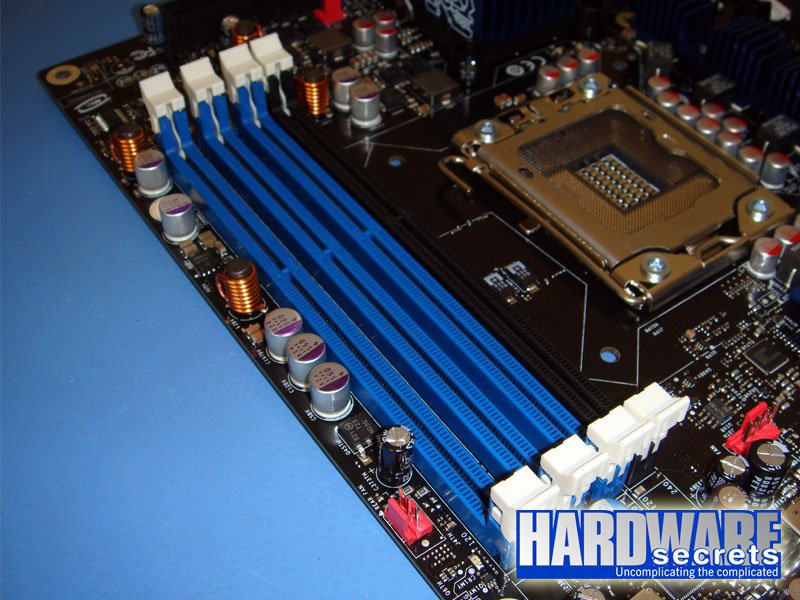
On motherboards with four memory sockets, you must install the memory modules sequentially, in the sockets with the same color. In fact, it is rather strange that these motherboards have four memory sockets, since if you install a memory module in the fourth memory socket, it will be accessed in single-channel mode. So, the fourth module will be left unused. See Figure 10.

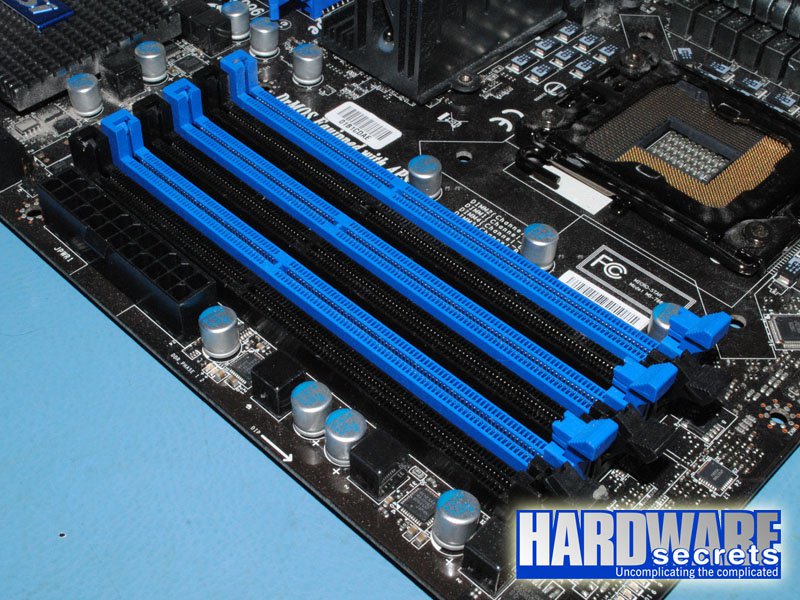
Motherboards with six memory sockets use the traditional scheme used by motherboards targeted to Intel CPUs. You must install the memory modules in the first, third, and fifth memory sockets, and these sockets almost always will use the same color, while sockets two, four, and six will use a different color. Therefore, simply install the memory modules in sockets with the same color. See Figures 11 and 12.

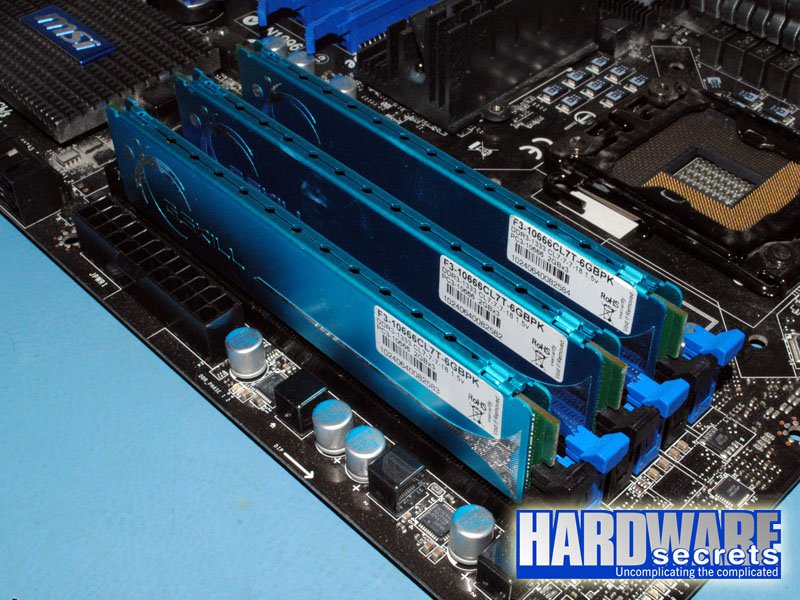
If you want to install six memory modules, the second group of memory modules must be installed in sockets two, four, and six unless all six modules are identical, in which case you will fill all six memory sockets and won’t need to worry about which sockets to use.
[nextpage title=”Quad-Channel Architecture”]
The quad-channel architecture quadruples the available memory bandwidth. This is done by expanding the memory data bus to 256 bits, which is accomplished by accessing four memory modules at the same time.
Currently, this mode is available only on the Intel socket LGA2011 (LGA2011) platform. This means that you can only enable this mode on motherboards and Core i7 CPUs that use this socket. These processors support DDR3 memories up to 2,133 MHz.
You will need four identical memory modules. Eight modules can be used on motherboards with eight memory sockets, and each group of four modules can have different capacities, but the modules inside the same group must be identical. If you install two or three memory modules, they will be accessed in dual- or triple-channel mode, respectively. Of course, in this case, you won’t achieve the maximum performance of which your system is capable.
There are two kinds of socket LGA2011 motherboards available: those with four memory sockets and those with eight or more memory sockets.
On motherboards with four memory sockets, simply fill all the sockets that are available.
Motherboards with eight memory sockets use the traditional scheme utilized by motherboards targeted to Intel CPUs. You must install the memory modules in the first, third, fifth, and seventh memory sockets, and these sockets almost always will use the same color, while sockets two, four, six, and eight will use a different color. Therefore, simply install the memory modules in sockets with the same color. On socket LGA2011 motherboards, usually half the sockets are at one side of the CPU socket, while the other half is on the other side. See Figures 13 and 14.
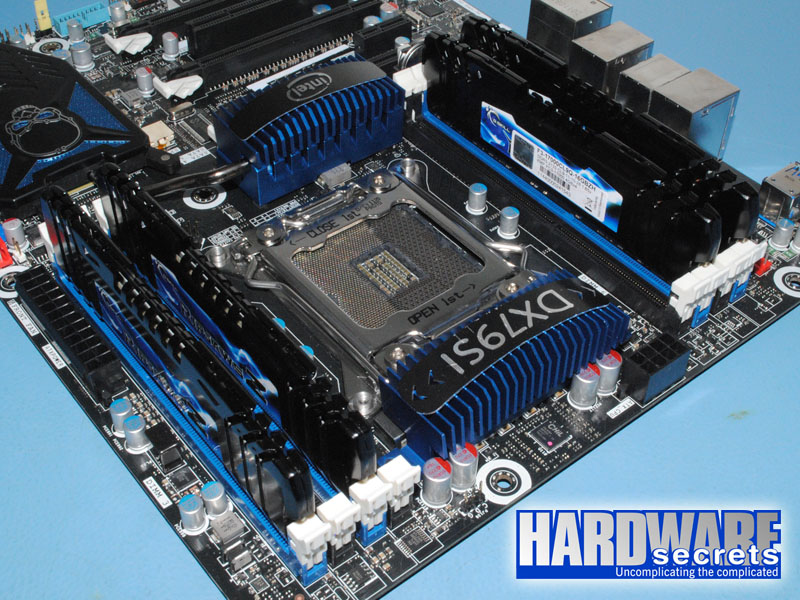
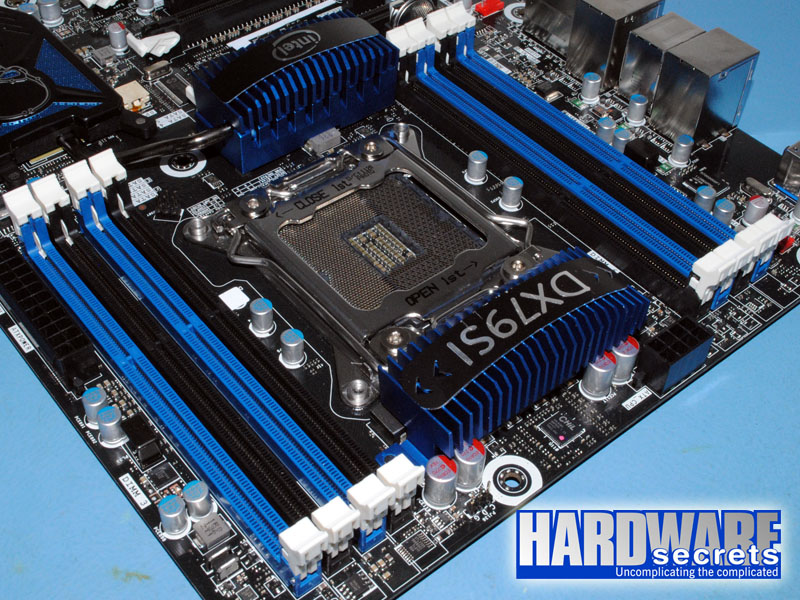

If you want to install eight memory modules, the second group of memory modules must be installed in sockets two, four, six, and eight unless all eight modules are identical, in which case you will fill all eight memory sockets and won’t need to worry about which sockets to use.
[nextpage title=”Checking if it is Correctly Enabled”]
After installing your memory modules, the final step is to check if the dual-, triple- or quad-channel architecture is correctly enabled.
Currently, most motherboards will display this information on POST, which is the screen that appears right after you turn on your computer, showing some information about your system. Look for phrases such as “Dual Channel” and “Single Channel.” See Figure 15.
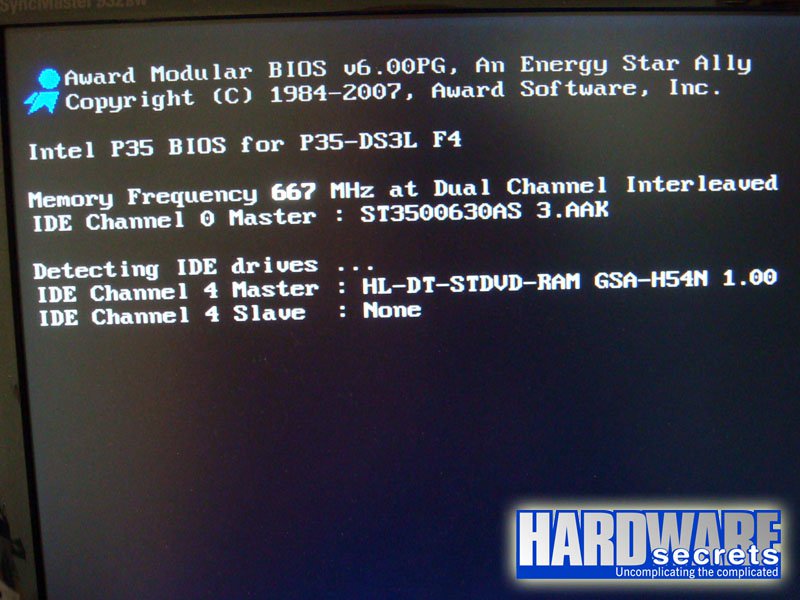
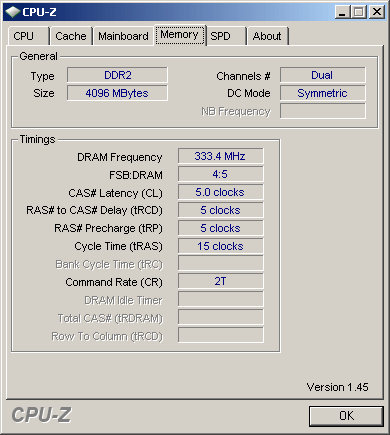
Another way to check this is by running a hardware identification utility. We recommend running CPU-Z and checking the memory information presented on its Memory tab, at “Channels #.” See Figure 16. On this same screen, you can check the current real memory clock rate and timings. Keep in mind that the real clock rate is half of the stated memory clock. In our example (Figure 16), the memories were being accessed at 333 MHz, i.e., “667 MHz.”
This is a good place to check if your memories are being accessed at their full speed. If not, you need to check to see what is wrong. (Usually there is a misconfiguration on the motherboard setup or a limitation of the CPU or chipset.)
Tip: Athlon 64 X2 5000+ Socket AM2 Review. Some older Athlon X2 processors have a problem where memories can’t be accessed at their full speed.

Leave a Reply